Canada is a country with rich and diverse geography. From the stunning coastline of the Atlantic Provinces to the rugged mountains of the West, there is something for everyone in this great country. This article will explore Canada’s seven geographic regions in detail.
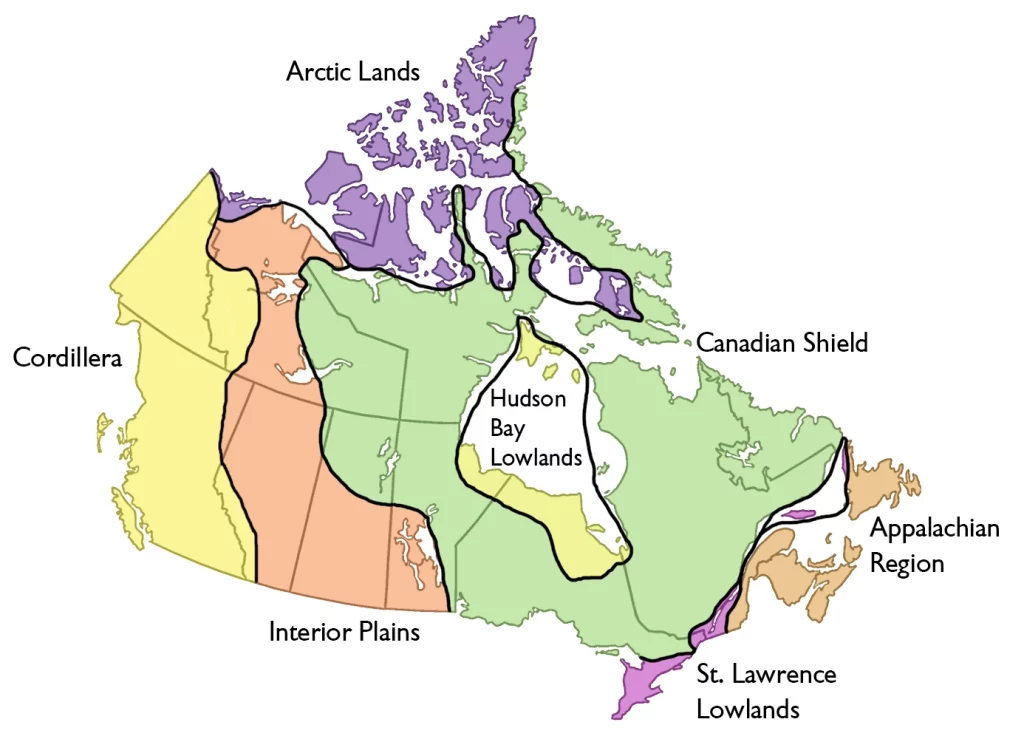
Canada is divided into seven physiographic regions: Arctic Lands, Cordillera, Interior Plains, Hudson Bay Lowland, Canadian Shield Forest Lands, St. Lawrence Lowlands, and Appalachia. Divisions are based on each area’s relatively similar physical geography.
Arctic Lands
The Arctic Lands region of Canada includes the northernmost parts of the country. It is a very cold and barren region, with most of the land covered in ice. Few people live in this region, as it is so inhospitable. However, some Indigenous peoples have traditionally lived in this region.
The Arctic Lands region is home to some of the world’s most iconic animals, such as polar bears and walruses. It is also home to the North Pole. This region is vital for global climate change research, as it is one of the places on Earth most affected by climate change.
Cordillera
The Cordillera is a region of Canada that includes the Rocky Mountains and the coastal mountains of British Columbia. This region is home to many landscapes, including forests, rivers, and lakes. The Cordillera is a popular destination for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and skiing.
The Cordillera has a diverse climate, depending on the elevation. The lower areas of the Cordillera are typically warmer, while the higher regions are more relaxed. The Cordillera receives a lot of precipitation, which helps to create its beautiful landscapes.
The Cordillera is an essential region of Canada, both culturally and economically. This region is home to many Indigenous peoples and several major cities such as Vancouver and Calgary. The Cordillera is also home to some of Canada’s most important natural resources, such as oil and gas.
Interior Plains
The Interior Plains region of Canada is located in the central part of the country. The Rocky Mountains border this region to the West, the Great Lakes to the east, and the Arctic Ocean to the North. This region has a diverse climate, with hot summers and cold winters. The Interior Plains is home to many animals, including bison, deer, and bears.
The Interior Plains region is divided into two sub-regions: Western and Eastern Interior Plains. The Western Interior Plains are dryer than the Eastern Interior Plains and experience more extreme temperatures. The Eastern Interior Plains are wetter and have a more moderate climate.
There are many different types of landscapes in the Interior Plains region. This region can all have grasslands, forests, lakes, and rivers.
Hudson Bay Lowland
The Hudson Bay Lowland is a vast area of low-lying land around Hudson Bay in Canada. This region is mainly covered in bogs and muskeg, with some forest areas. There are also many rivers and lakes in the Hudson Bay Lowland.
The Hudson Bay Lowland is home to a variety of wildlife, including caribou, moose, bears, and wolves. This region is also home to the Inuit people.
The Hudson Bay Lowland has a long history of human settlement. Aboriginal people have lived in this region for thousands of years. In the 1600s, European explorers and fur traders began to visit the Hudson Bay Lowland. In the 1800s, many settlers came to this region to start farms and homesteads. Today, the Hudson Bay Lowland is integral to Canada. This region is home to many different cultures and peoples. The Hudson Bay Lowland is also an important economic region, with many natural resources that are important to Canada’s economy.
Canadian Shield Forest Lands
The Canadian Shield is a large area covering much of northern Canada. It is made up of forests, lakes, and rivers. The forest Lands are a part of the Canadian Shield. They are located in the northern part of the country and are made up of coniferous trees. These trees include pine, fir, and spruce. The forest Lands are home to many animals, including bears, moose, and wolves.
The Canadian Shield is a vital region of Canada. It provides many resources that are vital to the country’s economy. These resources include timber, minerals, and water. The Canadian Shield is also a popular tourist destination. People come from all over the world to see its natural beauty.
St. Lawrence Lowlands
The St. Lawrence Lowlands is a geographical region in Canada that includes the St. Lawrence River valley and the Great Lakes. It extends from Montreal in the province of Quebec to Lake Ontario. The region is characterized by flat or rolling terrain, with some hills and mountains. The climate is moderate, with warm summers and cold winters.
The St. Lawrence Lowlands are home to a large portion of Canada’s population. Major cities in the region include Montreal, Toronto, and Ottawa. The region is also home to many important industries, including manufacturing, agriculture, fishing, and forestry.
The St. Lawrence Lowlands have a long history and have been inhabited by humans for thousands of years. The first peoples to inhabit the region were the Iroquois and Algonquin peoples. European settlement began in the 1600s, and the region has been part of Canada since 1867.
Appalachia
Appalachia is a region of North America that includes parts of the United States and Canada. The Appalachian Mountains stretch from Newfoundland to Alabama, and the region includes the states of Kentucky, Tennessee, Virginia, West Virginia, and North Carolina. In Canada, the Appalachian region includes the provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island.
Appalachia is known for its beautiful scenery and its rich cultural heritage. The Appalachian Mountains are home to many different plants and animals, and the region is also home to some important historical sites.
Description
The study of natural phenomena is what physiography used to be called. It is studied by physical geography and, more recently, in landforms. The process of defining regions is called physiographic regionalization.
The criteria used in the following physiographic regionalization are geologic structure, relief attributes of the land, the distribution of continuous permafrost, and the position of the treeline.
Combinations of these factors contribute to the seven regions that this article covers. These are Arctic Lands, Cordillera, Interior Plains, Hudson Bay Lowland, Canadian Shield Forest Lands, St Lawrence Lowlands, and Appalachia. These all belong to Canada and share similar physical geographical characteristics. Differences between them can be seen in satellite images. The areas quoted for these regions are hectares of land.
Google Maps of Canada
Interactive Google maps of Canada; Search for a place, zoom, look at the Street View, and create free driving directions with Google maps. Click here if you’re looking for free Driving Directions in Canada.