The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands is a natural region located in North America. It stretches from the eastern seaboard of the United States through the Great Lakes and into southeastern Canada. The area is home to some of the world’s largest freshwater lakes and many rivers and streams. The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands has a long history of human settlement. First inhabited by Native Americans, the region was later colonized by Europeans. Today, the area is home to many people of different cultures and backgrounds. The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands is an important economic region for Canada and the United States. The area is home to a large number of manufacturing plants, as well as many farms and mines. The region’s ports are also crucial for international trade. This blog post will explore the history, culture, and economy of the Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands.
This region of Canada is relatively small but has many towns and cities. It is milder in temperature than other parts of Canada and has rich soils. However, agricultural land is slowly being lost to urbanization. The Great Lakes are the world’s largest body of fresh water, and they’re linked to the Atlantic Ocean by the St. Lawrence River. Lakes Erie and Ontario’s moderating effects extend the Niagara Peninsula’s frost-free days, allowing peaches, grapes, and pears to grow extensively. Additionally, the waterways of the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River remain ice-free for much of the year, thus offering this inland region access to the Atlantic Ocean and other places of the world through a linking system of rivers and canals.
Location
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands is a physiographic province of the larger Laurentian Plateau that encompasses the Great Lakes Basin and the St. Lawrence River valley. The province extends from southwestern Quebec to northeastern Minnesota, covering an area of approximately 1.5 million square kilometers.
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands is bordered on the north by the Canadian Shield, on the west by the Plains of Abraham, and the east by the Appalachian Mountains. The province includes two major river basins – the Great Lakes Basin and the St. Lawrence Basin – and several smaller ones.
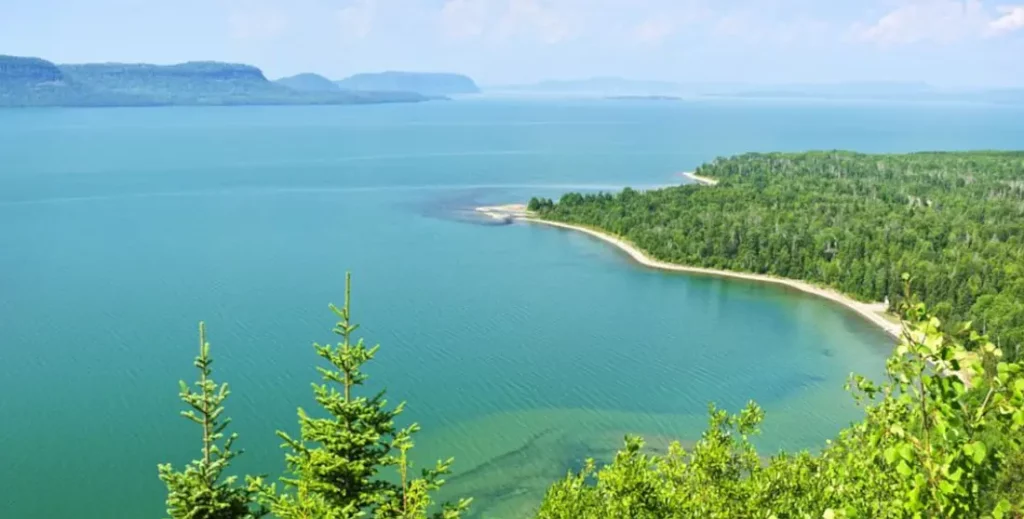

The Great Lakes Basin covers an area of more than 600,000 square kilometers (231661.07 sq mi) and includes all of the Great Lakes, as well as their tributary and outlet rivers. The Niagara River drains the basin, which flows into Lake Erie, and the Saint Marys River, which connects Lake Superior to Lake Huron.
The St. Lawrence Basin covers an area of more than 400,000 square kilometers (154440.71 sq mi). It includes parts of Ontario, Quebec, New York State, Vermont, New Hampshire, Maine, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania. The St. Lawrence River drains the basin, which flows into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence.
Natural Resources
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands is a unique and dynamic region of North America. The Great Lakes are the world’s largest freshwater lakes, while the St. Lawrence River is the world’s most comprehensive river system. This region is home to an incredible diversity of natural resources, including forests, wetlands, grasslands, freshwater lakes, and rivers.
The Great Lakes are a vital part of the regional ecosystem, providing habitat for various plant and animal species. The lakes also support a large commercial fishing industry, recreation, and tourism. The St. Lawrence River is an important transportation route for goods and people and a hydropower source.
Forests cover much of the Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands region, providing critical habitat for wildlife and timber for the industry. Wetlands are another vital part of the region’s ecosystem, playing a role in water purification and flood control. Grasslands are found in the less developed areas of the region, providing grazing land for livestock and wildlife habitat.
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands is truly a unique place on Earth, with an amazing array of natural resources that support a thriving economy and vibrant communities.
Climate
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands region has a continental climate, with warm summers and cold winters. The average temperature in the summer is 21°C (69,8 F), and in the winter it is -6°C (21,2 F). The Great Lakes region is one of the most humid areas in North America, with an average humidity of 70%.
Precipitation is moderate to heavy and falls equally throughout the year. However, the lakes tend to moderate the climate of the surrounding areas, making them warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer than other parts of Canada.
The Great Lakes region is also subject to severe weather conditions, such as tornadoes, thunderstorms, and blizzards.
Population
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands is home to over 50 million people, making it one of the most populous regions in North America. The region is home to some of the largest cities in Canada and the United States, including Toronto, Montreal, and Chicago.
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands is a highly urbanized region, with over 80% of the population living in urban areas. The region has a diverse economy, with major industries including manufacturing, healthcare, education, and tourism.
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands is a culturally diverse region with a significant immigrant population. The region is home to people from all over the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
Economy
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands region is home to Canada’s largest and most diverse economy. The region is a major hub for trade and transportation, with nearly half of all Canadian exports passing through its ports. The region also has a strong manufacturing base, accounting for more than a quarter of Canada’s manufacturing output.
The region’s economy is primarily driven by abundant natural resources, including forests, minerals, waterpower, and hydrocarbon deposits. These resources have helped the region develop a diversified economy that includes forestry, mining, energy, and manufacturing.
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands region is also home to Canada’s largest concentration of agriculture. The region’s mild climate and rich soils support various crops, including wheat, corn, soybeans, and vegetables. The region’s farms produce enough food to feed more than 40 million people.
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands region is one of the most populous regions in Canada. More than 20 million people live in the region, accounting for nearly 60% of the country’s population. The majority of the population lives in urban areas along the shores of the Great Lakes or the cities of Toronto and Montreal.
Tourism
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands is a beautiful and popular tourist destination. The area is home to many attractions, including Niagara Falls, the 1000 Islands, and the Great Lakes.
There are many different ways to enjoy the Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands. You can take a boat tour of the lakes, go fishing or swimming in them, or even enjoy the scenery from the shore. There are also plenty of museums and historical sites to explore in the area.
The Great Lakes- St. Lawrence Lowlands offers plenty if you’re looking for a more active vacation. There are many hiking and biking trails and canoeing and kayaking opportunities.
Whatever your interests, you can find something to do in the Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands.
Google Maps
Conclusion
The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands is a beautiful and diverse region of North America. The area is home to many different cultures and natural resources. The Great Lakes – St. Lawrence Lowlands is an important economic region for both Canada and the United States.