Formation: 1867. The origin of the name: Derived from the Iroquois Indian word Kanadario, meaning “sparkling water” or “beautiful lake.”
7 AM EST = noon GMT; 6 AM CST = noon GMT.
Ontario is Canada’s most populous province and home to the country’s capital, Ottawa. Ontario is also Canada’s economic engine, with a diverse economy including agriculture, manufacturing, and financial services. The province boasts 12 universities, two of which are among the oldest in North America.
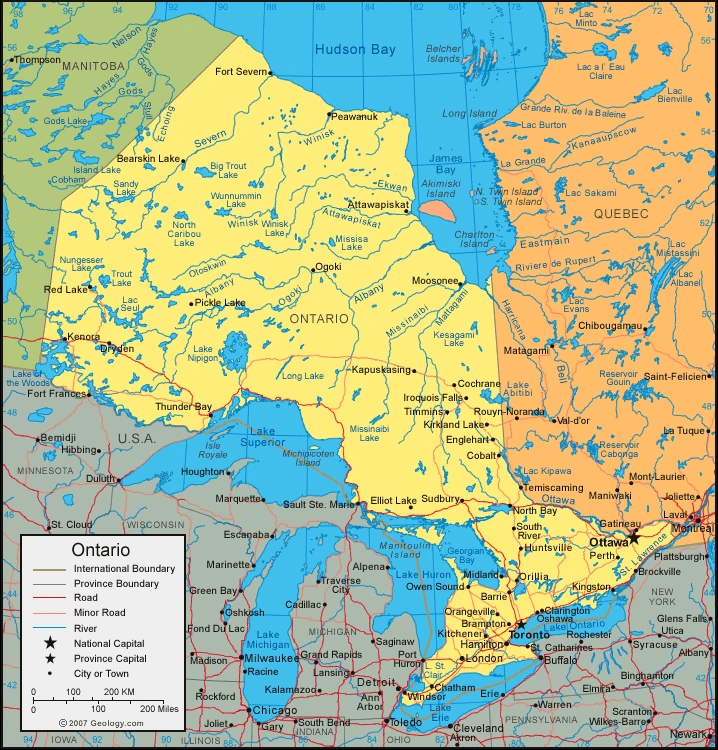
It has 14,571,494 people living there (2019). It’s also the third-largest province in size and is landlocked by Manitoba to the west, Quebec to the east, Hudson Bay to the North, and the U.S. state of Minnesota to the south. Ontario’s name originates from an Iroquois meaning “beautiful lake-filled land”. The province was first explored by Frenchman Étienne Brûlé in 1620 and later surveyed by John Innis as part of an expedition for a canal connecting Lake Superior and Lake Huron (1821).
Toronto, Ontario’s capital, is one of North America’s most extensive and diverse cities. The city is home to many different cultures, languages, beautiful buildings, museums, and landmarks.
Map of Ontario
Getting around Ontario
Two major highways interconnect Toronto and a few other major cities. One is Hwy 401, which runs from Toronto to Montreal in the east and Windsor in the west. The second is the Queen Elizabeth Way (QEW), which runs from Toronto to Niagara Falls. Buses also cover northerly routes.
The climate of Ontario
The relatively temperate climate across this region, from the south of Canada to the Great Lakes, is more severe in the east. In these areas, mean annual summer temperatures reach 72°f (22°c) because of the temperate climate and fertile soils that nurture Canada’s major agricultural industry. Ontario’s yearly average temperature is about 59 degrees. Winisk, the town closest to Manitoba, has a summer average of 54 degrees or 12 degrees Celsius. The warmest recorded temperature in Ontario was 108 degrees (42.2°c) in 1919, and the coldest recorded temperature was -73 degrees (-58.3°c) in 1935. In 72 hours during October 1954, Hurricane Hazel poured 7.8 inches (200 millimeters) of rain on Toronto and caused the worst flood in Canadian history.
Facts about Ontario
- Ontario is the second-largest province in Canada area. It takes up the strip of land on the Canadian mainland between Hudson Bay and James Bay to the North and the St. Lawrence River- Great Lakes chain to the south.
- Ontario is located to the East, South, and West of Quebec, the U.S., and Manitoba. To its, North lies Canada’s second-most populous province of Quebec. It is home to over one-third of Canada’s population.
- Having the country’s most natural resources, Ontario is also a prosperous province with a diverse and already developed industrial economy.
- The Northern and Southern Ontario regions make up the province of Ontario.
- Suppose a line is drawn from the Mattawa and Ottawa rivers, connecting them to the French River on Georgian Bay at the Quebec border. In that case, Northern Ontario usually will be north of this line.
- The Canadian Shield covers 950,000 square kilometers of the region and is characterized by lakes, rivers, bogs, forests, and rocky and rugged terrain.
- The treeline in Ontario is generally low, less than 1500 feet. The exception to this rule is Ishpatina Ridge, the highest point at about 2400 feet.
- The area has some of the wealthiest minerals and resources in all of Canada, which has led to the area’s wealth.
- Southern Ontario contains about 15% of the land area. Most of it is very flat.
- It is the lowest in the Ottawa River area and has its highest elevation point at about 1,770 feet in the Blue Mountains region south of Georgian Bay. The east is separated from the rest of the region by an extension of the Canadian Shield called the Frontenac Axis that crosses the St. Lawrence River east of Kingston and forms various lake districts such as Muskoka Lakes, lakes in Haliburton Highlands, and Rideau Lakes chain which are known best resort areas in Ontario.
- The most dramatic feature of the landscape is the Niagara Escarpment, running roughly northwest from Niagara Falls to the Bruce Peninsula.
- In Southern Ontario, most of the land has rolling plains. However, Eastern Ontario and Western Ontario are both relatively flat.
- The drainage basins of Northern Ontario are split by a higher area running from Lake of the Woods to Kirkland Lake. Major rivers in the northern system are the Severn, Winisk, and Albany, while significant rivers in the southern system include the Ottawa and French.
- Northern Ontario’s climate varies from the Great Lakes area, where frost-free weather is more than 100 days a year, to the Hudson Bay area, where the frost-free period can be as short as 40 days.
- In southern Ontario, there is a bit of variation. There are harsh winters, but the summers are generally warmer than in other regions. Ottawa receives approximately 600mm of snow and 35 degree Celsius in the summertime. The southern part receives less snow throughout the year, but the Ottawa Valley tends to be slightly more relaxed, with about 500mm of snow and 22 degrees Celsius in the summertime.
- Northern Ontario has boreal forests, but a tundra is at the northern extreme. Southern Ontario once had hardwood forests, but lumbering removed most of them during the 19th century.
- Numerous animal species live in Canada, including larger mammals, such as moose, woodland caribou, and black bears. There are also many small animals like porcupines, skunks, and rabbits. There are birds in Canada, including ducks, grouse, and hawks.
Google Maps of Ontario
Ontario is Canada’s second largest province in size, spanning over one million square miles. The northern part of Ontario is wild and untouched and can be reached by air, scenic roads, and railroads. The northern region is sparsely populated, unlike the fertile lands of southern Ontario, which many immigrants from the U.S. have come to explore. Toronto, Canada’s biggest city, and Niagara Falls, Canada’s leading tourist destination, are located in southern Ontario, near Lake Ontario.
Visit this page for driving directions in Canada.