Halifax is located in the province of Nova Scotia, Canada. The city has a population of about 440,000 and is known for its beautiful coastline, lively downtown core, and diverse culture. With so much to offer visitors, it’s no surprise that tourism is one of the critical industries in Halifax.
Nova Scotia is a province located on the east coast of Canada. The province consists of the mainland and Cape Breton Island. With its sparkling bays and ancient weathered fishing towns, Nova Scotia embodies the romance of the sea. The coastline is rugged and dramatic, with high cliffs and crashing waves. Inland, there are rolling hills, forests, and lakes. Nova Scotia is a popular tourist destination for its natural beauty, seafood restaurants, and friendly people.
The regional municipality comprises four former municipalities amalgamated in 1996: Halifax, Dartmouth, Bedford, and Halifax County.
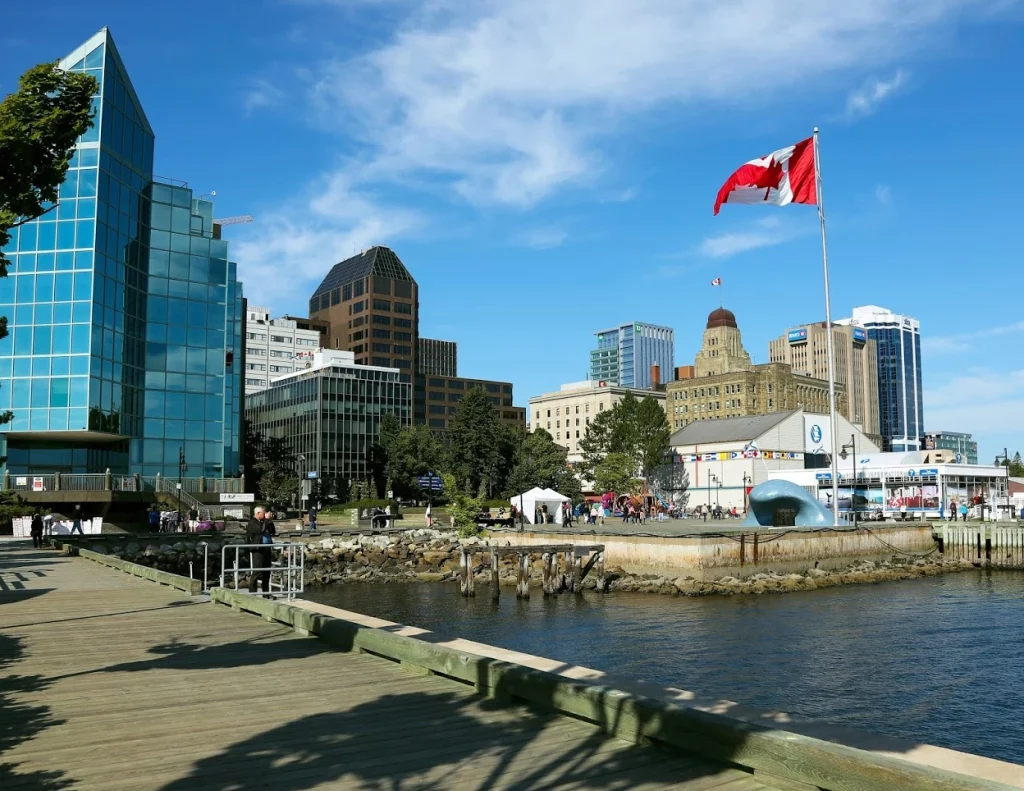

Halifax is the biggest city in the Maritime Provinces, but it ranks only tenth in size out of Canada’s ten most prominent cities. This doesn’t feel like it’s a big deal because Boston, San Francisco, and Toronto rank much higher in population than Halifax. These three cities feel connected and cohesive, making you forget that this is one of the main economic engines of eastern Canada.
Halifax is home to many businesses, the largest in the government or education sector. The city’s major employers are the national defense department, the university, hospitals, and the port of Halifax. The primary industries of the municipality are agriculture, fishing, mining, forestry, and natural gas extraction.
History
Halifax is located in the traditional ancestral lands of the Mi’kmaq people. Halifax, the Mi’kmaq name for “Great Harbour,” has been around since before Europeans arrived, who set up fisheries. Halifax was the first European settlement in the region. The Halifax Peninsula was named after the 2nd Earl of Halifax, where the capital of Nova Scotia was transferred from Annapolis Royal.
Halifax was established in 1749 and led to Father Le Loutre’s War. This happened when the British refused to acknowledge treaties with the Mi’kmaq people from 1726 after returning from Father Rale’s War. Canadian author Margaret Atwood is a feminist writer known for works such as “The Handmaid’s Tale (1985).” Settlement centers such as Halifax, Bedford, Dartmouth, and Lawrencetown were built to safeguard them from attacks by the Mi’kmaq, Acadians, and French. Settlements were made for refugees who migrated to Lunenburg during the American Revolution.
The SS Mont-Blanc, a French cargo ship carrying munitions, collided with the Belgian Relief vessel SS Imo in The Narrows between upper Halifax Harbour and Bedford Basin, creating one of the most significant disasters in Canadian history. The Halifax Explosion was an enormous artificial explosion before the development of nuclear weapons and resulted in almost 9,000 injuries.
Before 1996, the Halifax urban area’s four municipalities had a municipal government. Regional amalgamation occurred on April 1 of that year, creating one municipal government for the whole Halifax County except for First Nations reserves.
The region is now known as the Halifax Regional Municipality, but most refer to it by its former name, “Halifax”. On April 15, 2014, people approved a new branding campaign for the region created by Revolve Marketing. Local citizens prefer the city to be called simply Halifax, but the official name is still Halifax Regional Municipality. The proposed rebranding was met with mixed reactions from residents. Some felt the change would alienate other communities in the municipality, while others were relieved that they no longer had to use the longer formal name.
Geography
Halifax is located in the eastern part of Nova Scotia. The Halifax Regional Municipality borders the city to the south, the Municipality of Dartmouth to the southwest, the Municipality of North Bedford to the west, and the Municipality of Cumberland to the north.
The County of Halifax is an English county dating back to 1066 when it first served as a royal fiefdom. The County has two distinct divisions – rural and urban. In 1996, the County was amalgamated into the larger municipality – Halifax Regional Municipality. As of 2021, the total surface area for HRM is 5,475.57 sq km at 2114.13 sq mi. The urban space only comprises 8% of this surface area (238.29 sq km).
Halifax Regional Municipality is comparable in size to Prince Edward Island and measures over 660 kilometers in length. The nearest point of land to Sable Island is not in HRM but in Guysborough County. However, the islands are considered part of the Halifax Regional Council.
The coastline is heavily indented, causing it to be 250 mi / 400 km long. The municipality’s population is 50-60 mi / 31-37 km, and the coast is mostly rocky with small sand beaches. The municipality consists of various landscapes, including farmland and rocky areas. Towns include Musquodoboit Valley, Cole Harbour, and Sheet Harbour. The area has many waterways and islands.
Google Maps of Halifax
Climate
The Halifax area has a humid continental climate that borders on a marine climate, providing warmer summers and milder winters. This is due to synergistic effects from the warm gulf stream and temperature variations inland. January is the coldest month at around −0.1°C, while August is the warmest with a high of 1.8°C. The sea heavily influences the climate with significant variations in summer temperatures due to seasonal lag and differences in daylight hours, with September being the third mildest month (only colder than June).
Precipitation is high year-round. Winter features a mix of rain, freezing rain, and snow. The winter of 2014 to 2015 was the most recent, with colder temperatures and more snow than usual in a very long time. Eastern Canada often experiences cool weather and late springs compared to Western Canada, given its geographic location. This is because of the sea temperature, which often cools the climate. Despite this, summers in Eastern Canada are typically hot, with mild temperatures in Autumn.
Average monthly rainfall is the highest from November to February and is caused by intense fall/winter storms. The lowest rain content is in the summer, with August being the year’s warmest and driest month.
Halifax is more susceptible to hurricanes because it has been getting hotter. In 2003, Hurricane Earl created considerable damage along Halifax’s coast, and this time around, Hurricane Dorian made landfall just south of Halifax, causing significant damage.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Halifax was 99 degrees Fahrenheit. In 1912, it reached 37.2 degrees Celsius (99.0 degrees Fahrenheit). However, the coldest temperature recorded in Halifax was 20 degrees Fahrenheit. On March 22, 2012, when Canada experienced a heat wave, the temperature soared to 80 degrees Fahrenheit (28 Celsius) at the weather station in Halifax Windsor Park and 81 degrees Fahrenheit (27 Celsius) at Halifax Stanfield International Airport. Out of all years with above-average temperatures in Halifax, only one day goes up to 86 degrees Fahrenheit. Despite this, Nova Scotia has more frost than other Canadian provinces due to the maritime influence on their climate. The cold season lasts from October 31 until May 1 and averages 48 days unless they get hit by snow storms which last until April 16 typically.
Municipal landscape and communities
The Halifax Regional Municipality includes four municipal governments, the urban and rural areas. Two hundred communities within the former County of Halifax have maintained their original geographic names, including the dissolved cities of Halifax,,, Dartmouth, and Bedford.
The Halifax Regional Municipality is divided into eighteen communities, with each area being further subdivided into neighborhoods or villages. The regional municipality has reduced duplicate street names, such as 9-1-1 dispatch services. At the time of amalgamation, some street names were duplicated several times throughout the municipality.
One of the best parts about Halifax is its high-quality neighborhoods. One of them, Spring Garden, is a lively mixed-use neighborhood with plenty of shopping and entertainment options and the new Halifax Central Library. There has been a new trend in development happening in the North End, with many new housing projects built on surface parking lots. It is multicultural and artistic but has a long history centered around several community nodes, including the venerable Göttingen Street and Hydrostone commercial areas. The Quinpool District is the heart of Dartmouth and comprises residential, commercial, and public spaces. Downtown Dartmouth has restaurants and shops, a renovated Dartmouth Marine Slips housing the King’s Wharf neighborhood, and North Preston outside the city.
Halifax’s peninsula is known for its high walkability. Halifax has many mixed-use compared to suburbs with highly segregated areas, contributing to its vibrancy and convenience. The municipality has recently begun focusing more on building widespread cycling infrastructure.
Culture
Halifax is a vibrant, cosmopolitan city with a rich history. From its days as a fishing and shipbuilding community to its present-day status as Canada’s largest urban center, Halifax has always been a place of change and growth.
The city is home to many distinctive neighborhoods, including the North End, the artisan district of Clayton Park, and the historic Lower Town district. Halifax is also known for its art scene, which includes renowned galleries like the Art Gallery of Nova Scotia and the Musqueam Art Gallery. Halifax is a great place to live, work, and play. There’s never a dull moment in this lively city with plenty of activities and attractions to keep everyone entertained.
Halifax hosts many festivals throughout the year, including the largest Canada Day celebration east of Ottawa, the Atlantic Film Festival, the Halifax International Busker Festival, Greekfest, the Atlantic Jazz Festival, and the Multicultural Festival. The city’s Pride event is one of Canada’s most prominent LGBT events and is world-renowned.
There are many performance venues in Halifax. The Neptune Theatre is one of the largest, as it holds a variety of plays year-round. Shakespeare by the Sea performs nearby at Point Pleasant Park, while Eastern Front Theatre can be found in Downtown Dartmouth (accessible by ferry from Halifax Central Library). There are also smaller options, like Spatz Theatre and Bella Rose Arts Centre located within Citadel High School and Halifax West High Schools.
Many American and Canadian films have been generated in Halifax and have since become an important production center. The CBC has its broadcasting centers in Halifax, which are used for radio and television broadcasts. In 2020, filming began on Pub Crawl, which explored the historically significant bars of Halifax.
Completed in 1996, the Halifax Central Library on Spring Garden Road has been praised for its architecture and is currently lauded as a new cultural icon. It offers many community facilities, including an auditorium with 300 seats.
Tourism
Halifax’s tourism industry showcases Nova Scotia’s culture, scenery, and coastline. There are several museums and art galleries in downtown Halifax. The Canadian Museum of Immigration at Pier 21, an immigrant entry point prominent throughout the 1930s, 1940s, and 1950s, was opened to the public as a National Historic Site of Canada in 1999 and is the only national museum in the Atlantic provinces. The Maritime Museum of the Atlantic is a maritime museum containing extensive galleries, including a large exhibit on the famous Titanic, over 70 small craft, and a 200-foot (61 m) steamship CSS Acadia. In the summertime, the preserved World War II corvette HMCS Sackville operates as a museum ship and Canada’s naval memorial. The Art Gallery of Nova Scotia is housed in a 150-year-old building containing nearly 19,000 works.
The Halifax waterfront is the site of many popular attractions, including a boardwalk and ferry terminal. During the annual Halifax International Busker Festival, buskers perform in public squares.
It’s very easy to access a wide array of interesting restaurants. Two malls near Downtown Halifax are the Park Lane Mall and Scotia Square. There are 200 restaurants in total. In addition, there is Maritime Mall and Barrington Place Shops, among others. For cafes, there are also many that open in the summertime. This area has a lot of nightlife, with many bars and music venues. The large Casino Nova Scotia is also located nearby on the waterfront.
Demographics
In 2021, the Halifax Regional Municipality had a population of 439,819, living in 190,512 of its 200,473 total private dwellings. Comparing that to 2016’s population of 403,131, it increased by 9.1%. The population density was 80.3/km2 in 2021.
At the time of the 2021 census, Halifax had 465,703 people living in 201,138 out of 211,789 total dwellings. They had a population density of 64 people per square kilometer in 2021.
As of 2021, Halifax has a population of 348,634. They live in 154,883 homes, which is considered to be the urban core of Halifax. This area’s population density is 1,463 people per square kilometer.
There are many religious institutions in Halifax, such as St. Mary’s Basilica, New Horizons Baptist Church, St. George’s (Round) Church, United Rockingham Church, and more. These all create a diverse society in Halifax.
Economy
The Halifax Regional Municipality’s economy is primarily service-based. The municipality’s diversified industrial base includes shipbuilding and aerospace, clothing and textile manufacturing, and food processing. Tourism is also an essential part of the economy, with visitors drawn to the city’s heritage, attractions, and natural beauty. The Halifax Regional Municipality also has a solid financial services sector.
Major employers around Halifax include the Department of National Defence, the Port of Halifax, Irving Shipbuilding, and more. The supply chain in Halifax has also been a significant economic generator in the city, increasing in recent years. These successes have led to new property developments and revitalization efforts in some working-class areas.
Many resource industries in Halifax largely take place in rural areas. There are 150 families operating farms in Halifax, most of which are located in the Musquodoboit Valley. In addition, fishing is happening along the coastlines with independent fishing harbors, such as Sheet Harbour Industrial Port.
In Halifax, natural gas is extracted from Sable Island, and mining resources are extracted in rural areas. Limestone mines are extracted in the Musquodoboit Valley, and gold is extracted from the Moose River.
Government
A mayor and a 16-person council govern the Halifax Regional Municipality. The mayor is elected at large, and the district elects the councilors. Council oversees all facets of municipal government, including the police, libraries, fire department, water commission, public works, garbage management, and planning. Planning and development files, in particular, must be approved by provincial legislation.
There are three community councils to help make decisions in the city. Each council is made up of a few regional councilors that offer input from other areas.
Halifax is the capital of Nova Scotia and is home to the Nova Scotia House of Assembly. It’s also hailed as one of the finest examples of Palladian architecture in North America, which meets in Province House.
Transportation
Halifax Harbour is a major port used by numerous shipping lines. The Royal Canadian Navy and the Canadian Coast Guard have significant Halifax installations. There’s also a public ferry service connecting downtown Halifax to two locations in Dartmouth and one more in Sheet Harbour, serving industrial users.
The Halifax Port Authority’s various shipping terminals constitute the eastern terminus of the Canadian National Railway’s transcontinental network. Via Rail Canada provides overnight passenger rail service from the Halifax Railway Station three days a week. The Halifax Railway Station also serves as the terminus for Maritime Bus, which provides transportation across the Maritimes.
Halifax Stanfield International Airport is Canada’s eighth busiest airport by passenger traffic. One of their runways is dedicated to helicopters from CFB Halifax, which serve as the Royal Canadian Navy’s aviation component.
There are two bridges, the Angus L. Macdonald and A. Murray MacKay suspension bridges, and an extensive highway system allowing quick travel from one point in the core to another. Although efficient, these highways can also cause traffic jams at times of higher use.
Public transit in Halifax is provided by Halifax Transit, which operates buses and ferries throughout the region. Established in 1752, the municipality’s ferry service is North America’s oldest continuously running saltwater service.
Conclusion
Halifax is a fantastic city with a lot to offer visitors. From its beautiful waterfront and vibrant downtown core to the rolling hills of the North Shore and the bustling suburbs, there is something for everyone in Halifax. If you’re looking for accommodation options, check out our selection of hotels in Halifax. Alternatively, if you’re interested in activities and attractions, explore our listing of things to do in Halifax. We hope this article has helped you understand what awaits you when you visit Halifax next!